Encapsulation Explained
Encapsulation is one of the core pillars of object-oriented programming (OOP). It refers to the concept of combining data (fields) and the functions that work on that data (methods) into a single unit
Encapsulation = Hiding internal details + Allowing controlled interaction (Restricting access)
Real-World Analogy
Imagine a vending machine. You don’t open it up to grab snacks or fiddle with the money system inside.
Instead, you use the buttons and coin slot interface.
The machine gives you limited, predefined options: insert money, select an item, get your snack.
You never see how the inventory is tracked or how the change is calculated.
Internally, the company may redesign how the machine handles inventory or payments, but your experience as the user stays consistent.
How Encapsulation Is Done in Code
Encapsulation in programming is usually achieved by:
Access Modifiers (
private,protected,public)Getters and Setters for controlled interaction
Why Encapsulation Matters
Encapsulation is important because it makes systems secure, maintainable, and flexible. Specifically:
Data Hiding – sensitive details stay shielded from accidental or malicious misuse.
Controlled Access & Security – rules and validation can be enforced before state changes happen.
Maintainability – you can update or optimize the inner logic without breaking external code that uses the class.
External code doesn’t care how something works internally; it only needs to know what it can do.
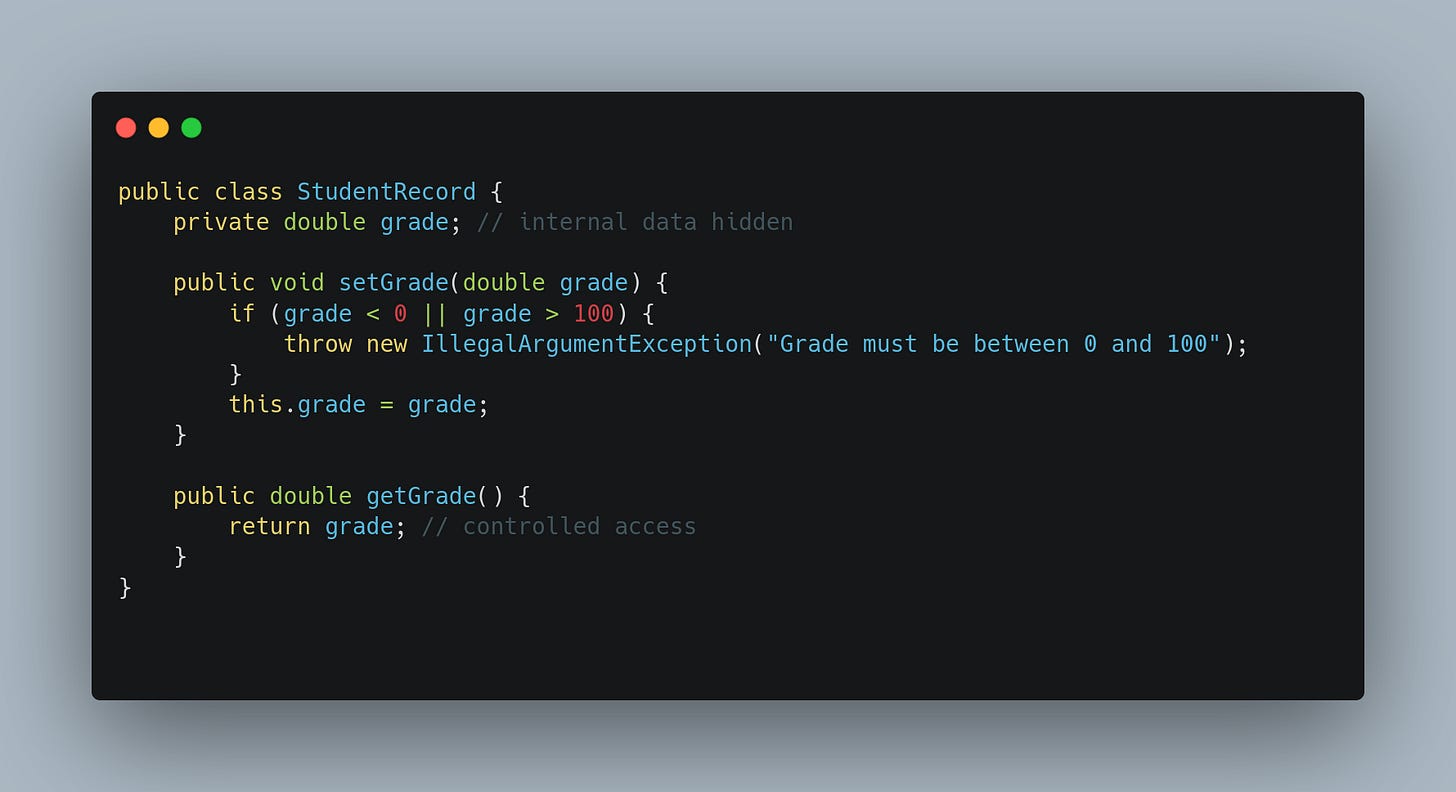
Code Example 1: StudentRecord
Suppose we’re building a system for a university. Students have grades, but we don’t want outside code to modify grades directly without validation.
Note : At any point you like to copy the code and run it for yourself click the image that has the code. It will take you to a github gist with the code.
The field
gradeis private.setGrade()validates the input before updating.getGrade()safely provides read-only access.
This ensures student grades remain valid and consistent.
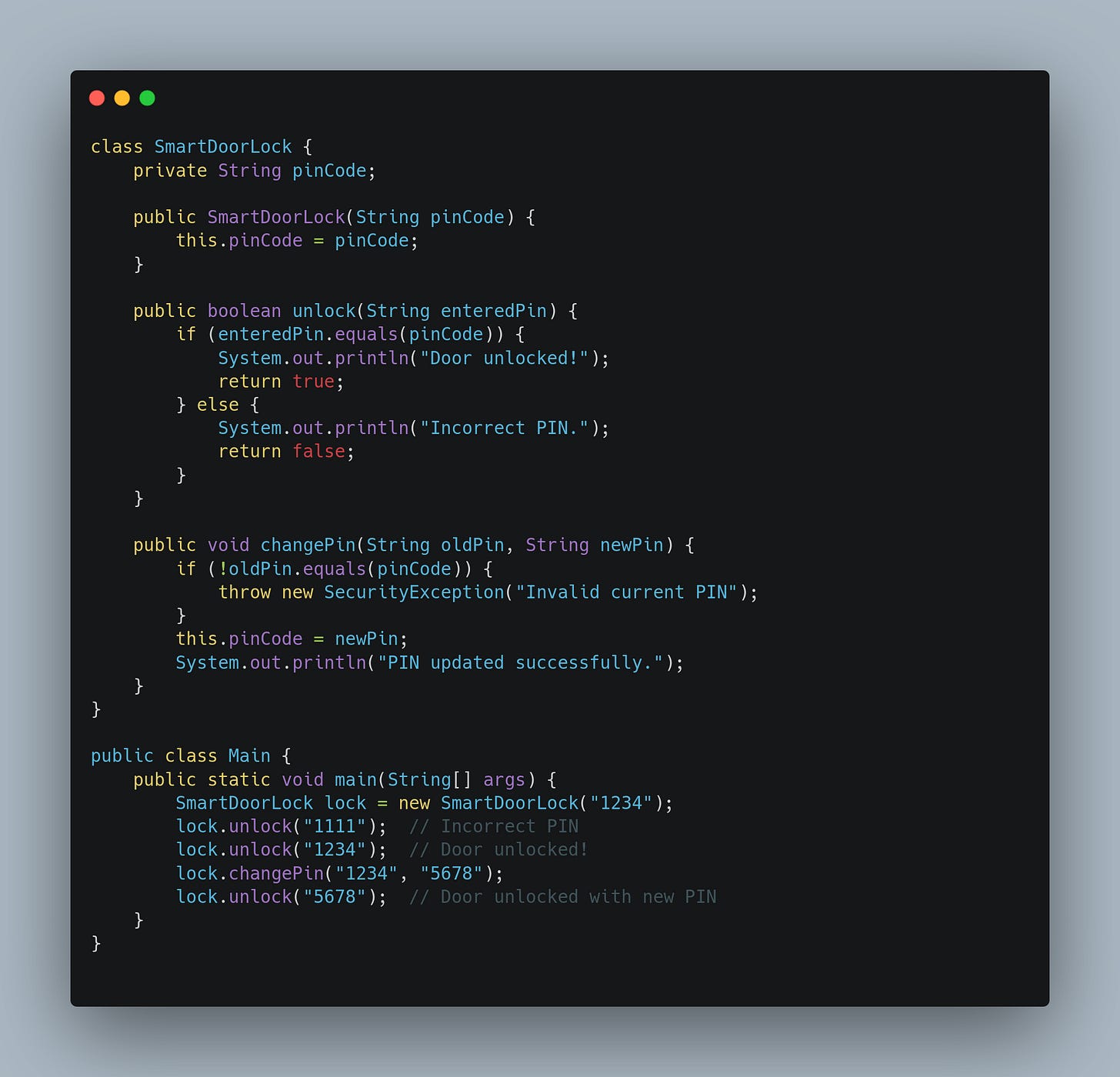
Code Example 2: SmartDoorLock
A smart lock should let you unlock a door with a PIN code but never expose the actual stored password directly.
Why this works:
The actual
pinCodeis hidden and can’t be accessed directly.Only
unlock()andchangePin()provide controlled access.The logic ensures the lock can’t be tampered with externally.
Keep Grinding I will see you in the next Read